History of Asbestos Use in Louisiana
The timeline of asbestos exposure in Louisiana highlights the state’s long history of industrial and construction-related asbestos use. This widespread use of asbestos has left a lasting impact on our community, with many residents and tradesmen facing the consequences today through asbestos-related diseases, like mesothelioma.
1930s
Early Use of Asbestos and Industrial Expansion
Asbestos-containing materials begin to be used in construction and commercial products.
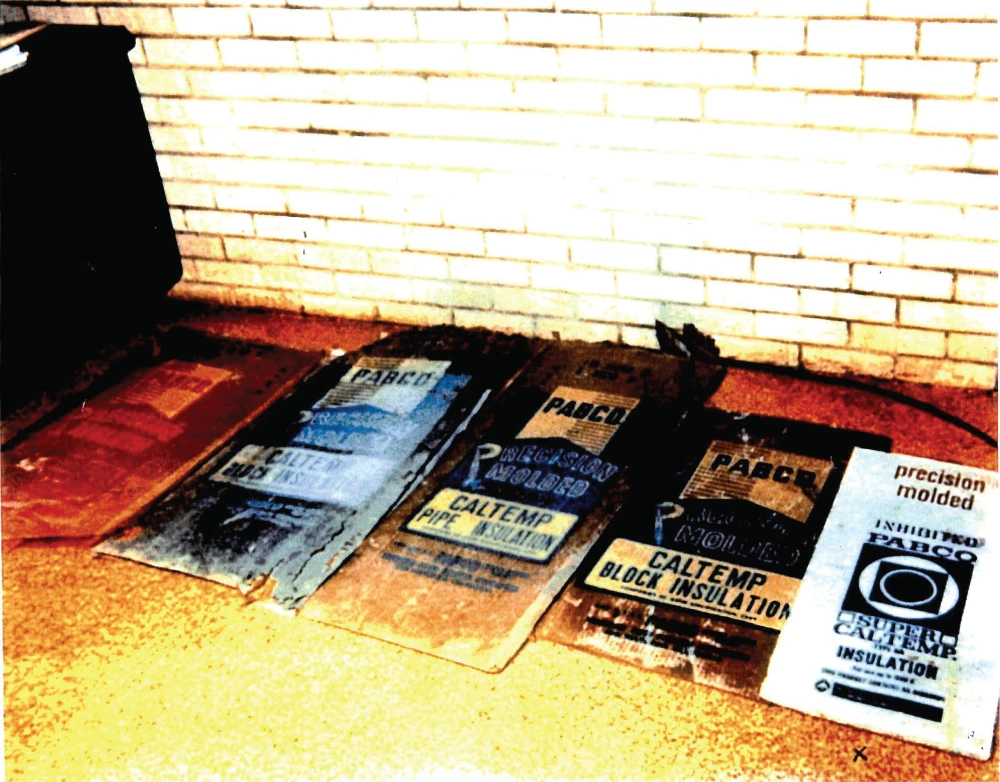

Oil refineries across Louisiana used numerous asbestos-containing products, particularly the high-temperature thermal insulation for the piping systems.

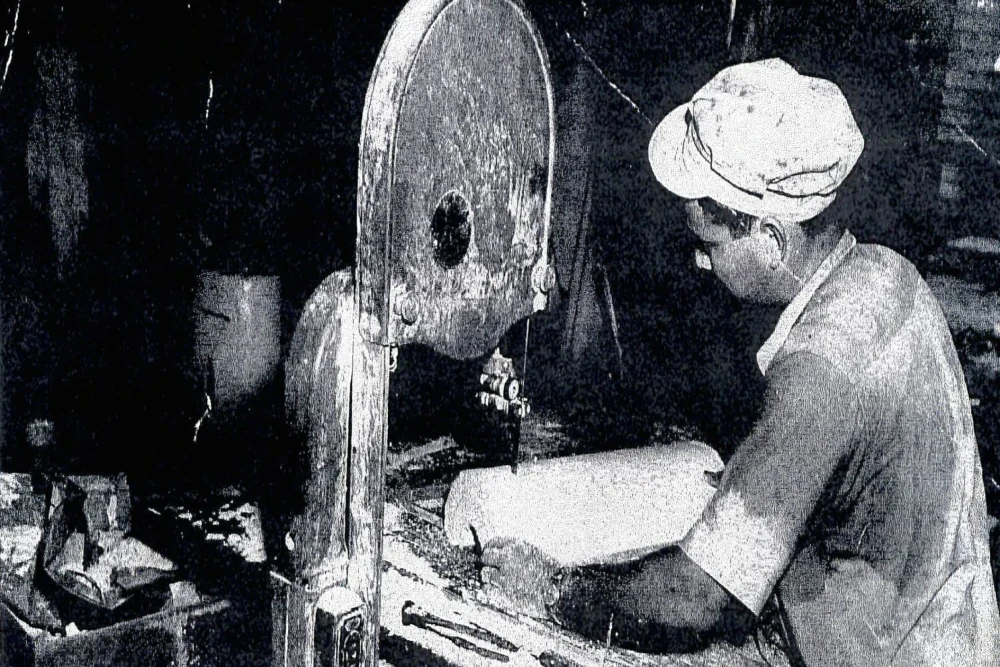
Louisiana led the entire country in timber production, and the papermaking industry employed asbestos in numerous ways right from the start.

1930s
Manufacturers Have Known of the Dangers of Asbestos
However, manufacturers failed to warn workers of the dangers or place warning labels on their products.
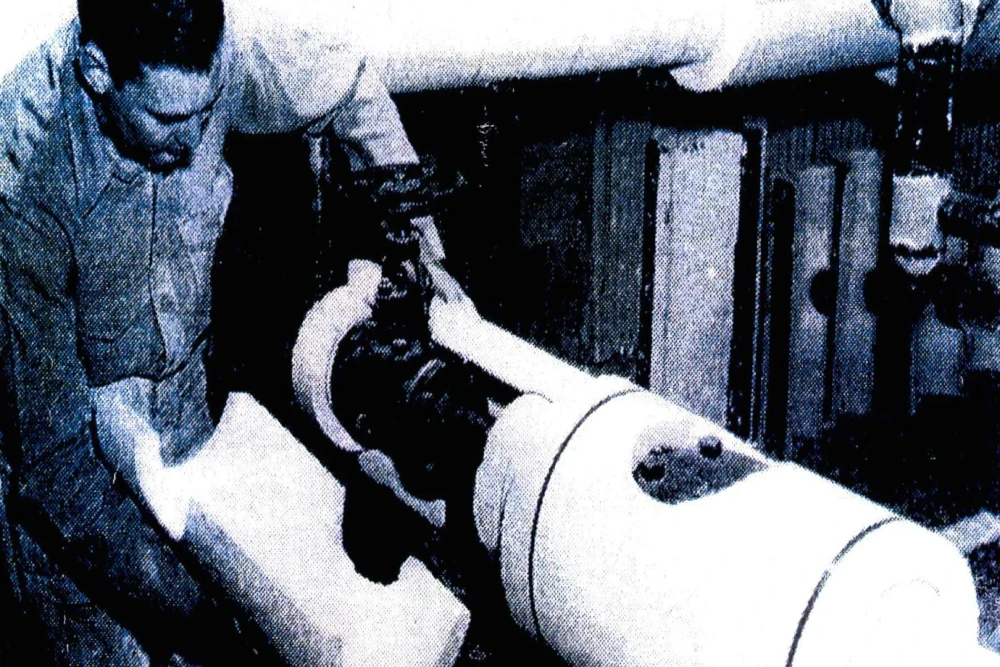
No protective gear was provided for workers in many industries like oil refineries, shipyards, and construction.
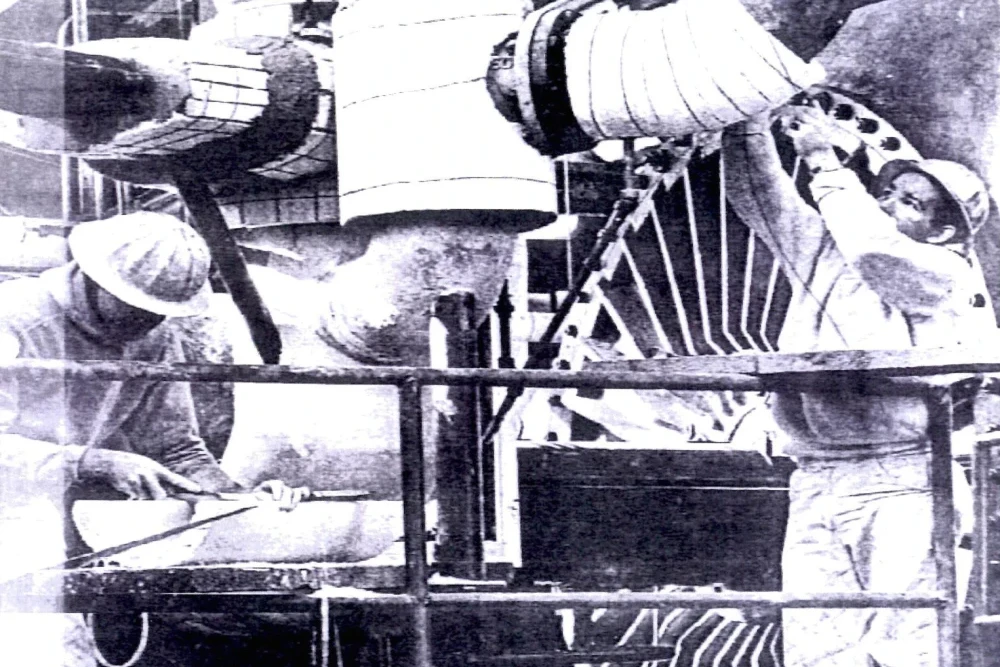
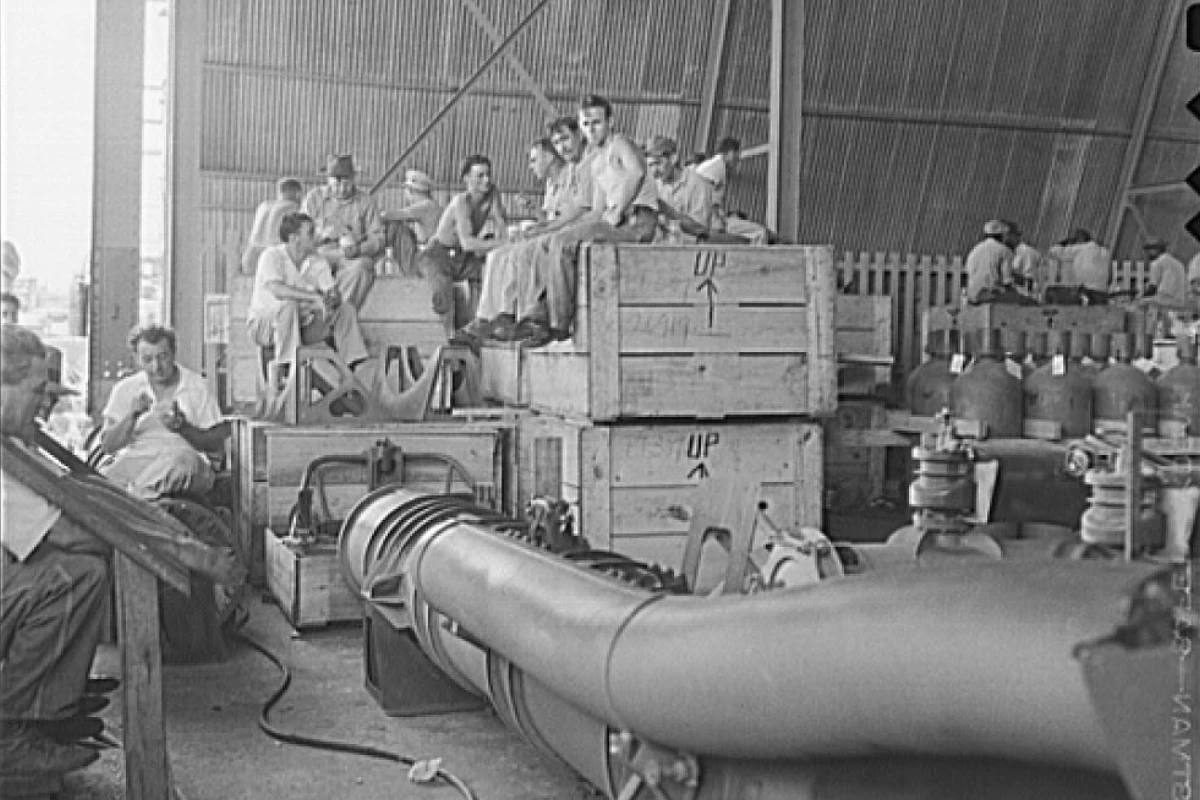
1938
Avondale Shipyard Begins Operation
Avondale Shipyard quickly became the largest employer in Louisiana.
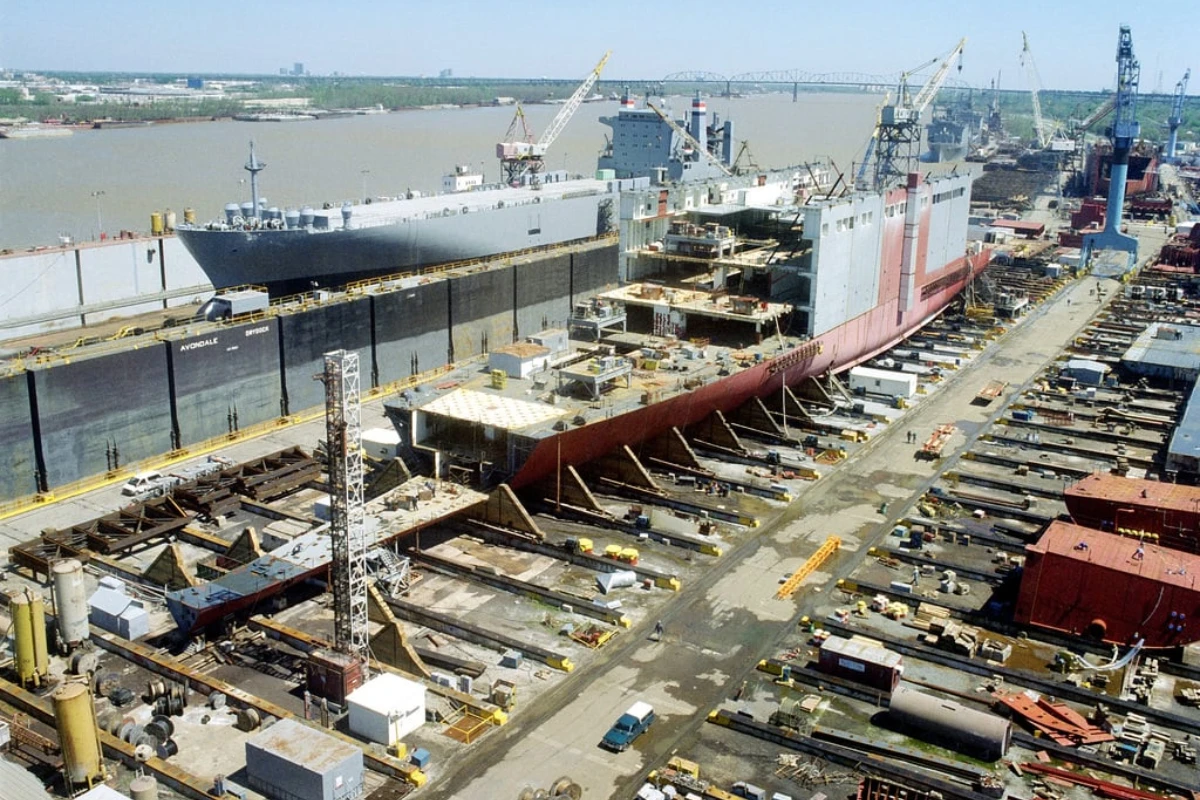

Thousands of Avondale workers were exposed to asbestos during the construction and demolition of ships.
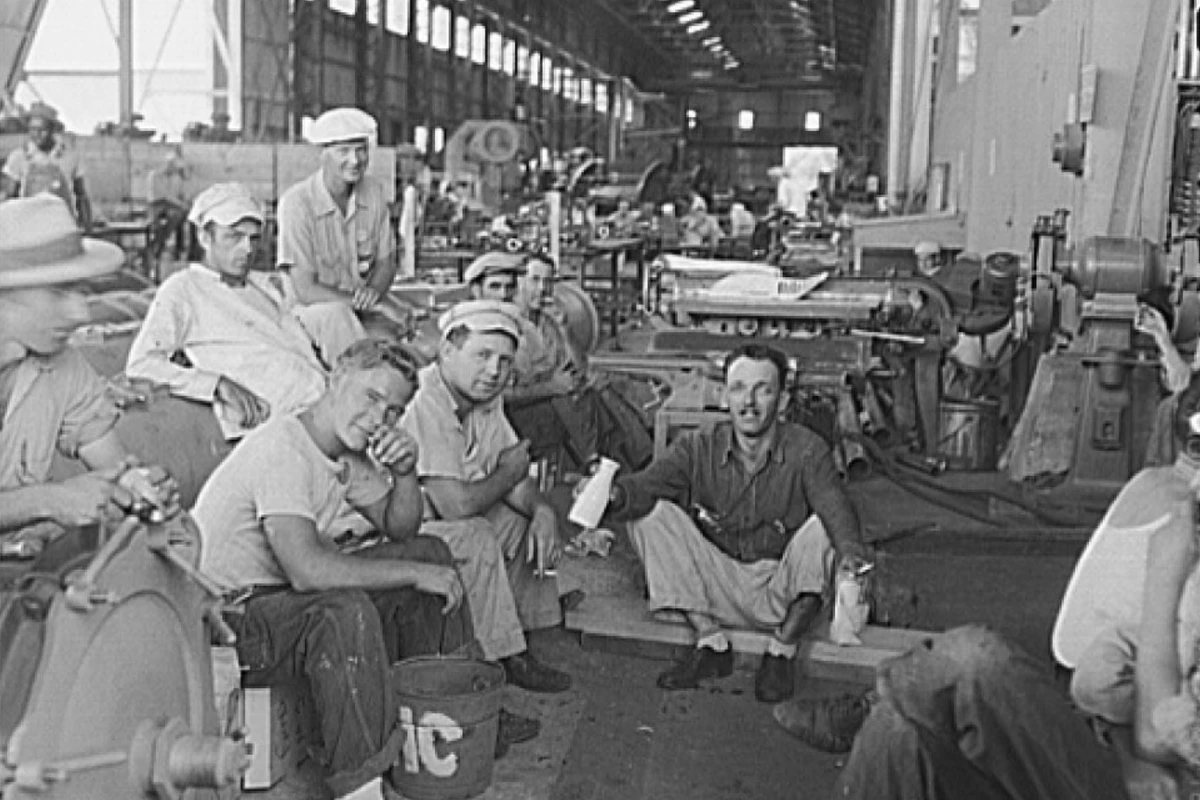

Avondale Shipyard saw a peak in activity during WWII.
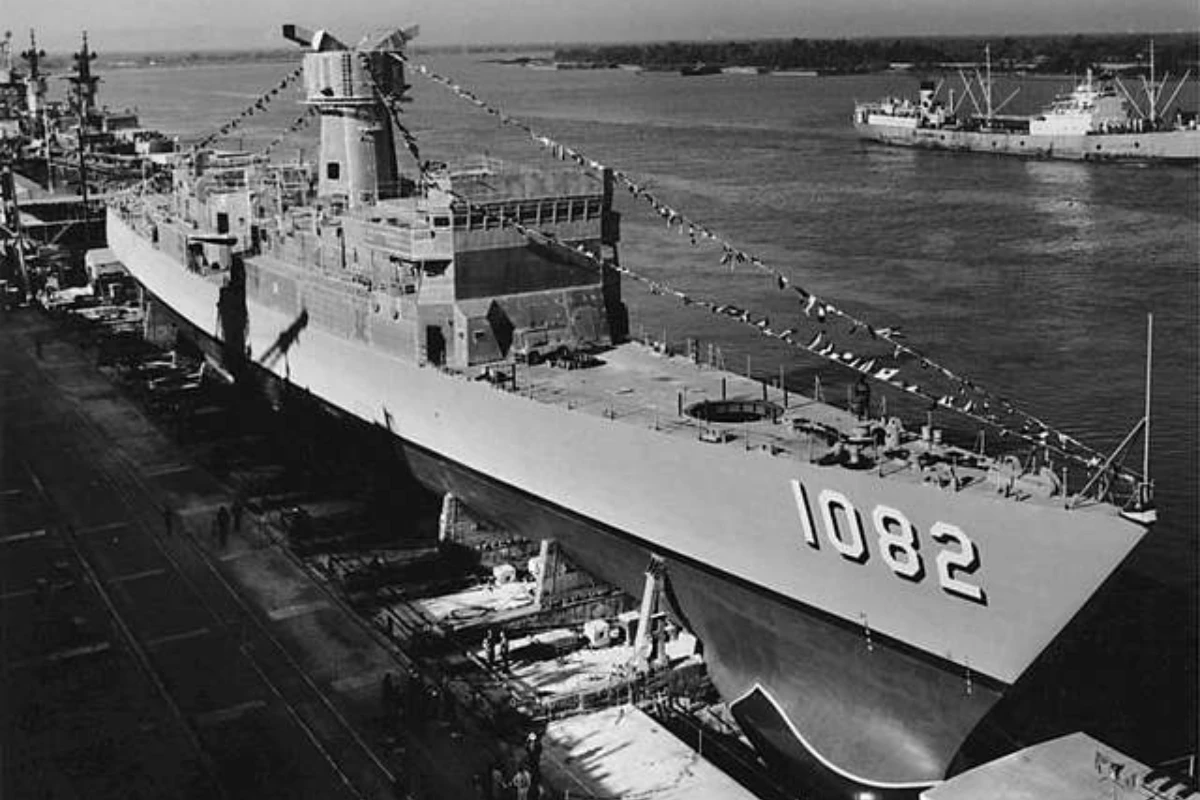

More mesothelioma victims have worked at Avondale Shipyard than at any other job site in Louisiana.

1942
ExxonMobil Oil Refinery Begins Operation of Fluid Catalytic Cracking Plant in Baton Rouge
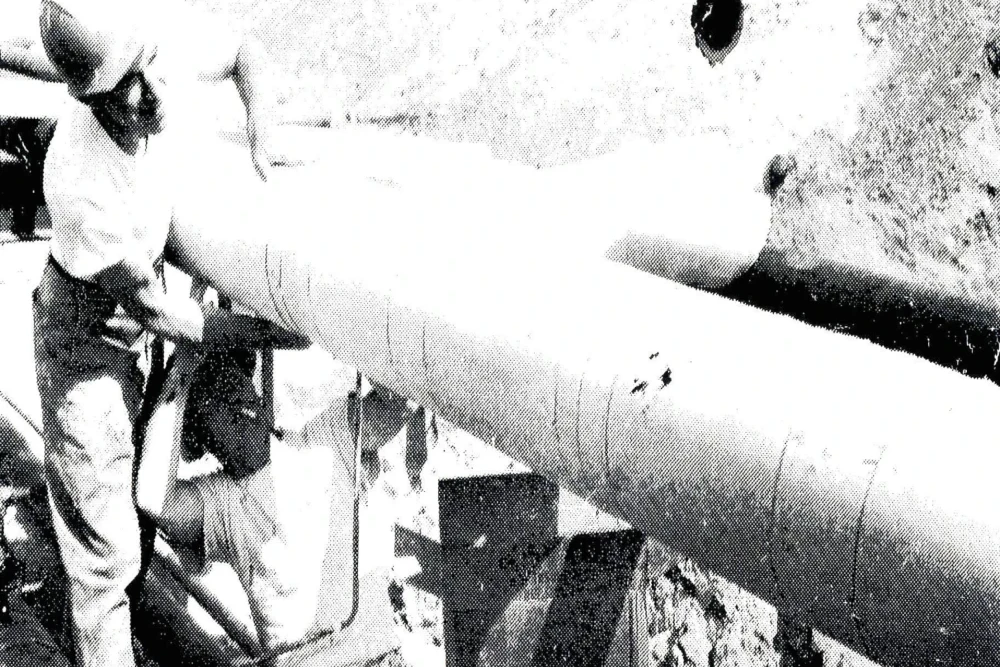
During the construction and operation, workers were tasked with installing, repairing, and maintaining miles of pipe that was heavily insulated with asbestos-containing materials.

1940s
Asbestos Use in Military Peaks During World War II
Nearly all branches of the military used asbestos, including in the construction and repair of Navy and Coast Guard ships.
U.S. Navy veterans who served aboard ships are more likely to develop mesothelioma than other branches of the military and civilians.

1945
Post-War Expansion and Asbestos Use
Post-WWII Housing Boom
After WWII ended, housing construction across Louisiana dramatically increased as servicemembers returned home and needed homes to raise their families.

From 1940 to 1960, Louisiana’s population grew by nearly 100,000.

The housing industry skyrocketed nationwide, and the Louisiana landscape transformed with the creation of thousands of mass-produced suburban tract homes.

Asbestos-containing products such as floor tiles, roof shingles, plasters, and drywall products were used in the construction of these homes.

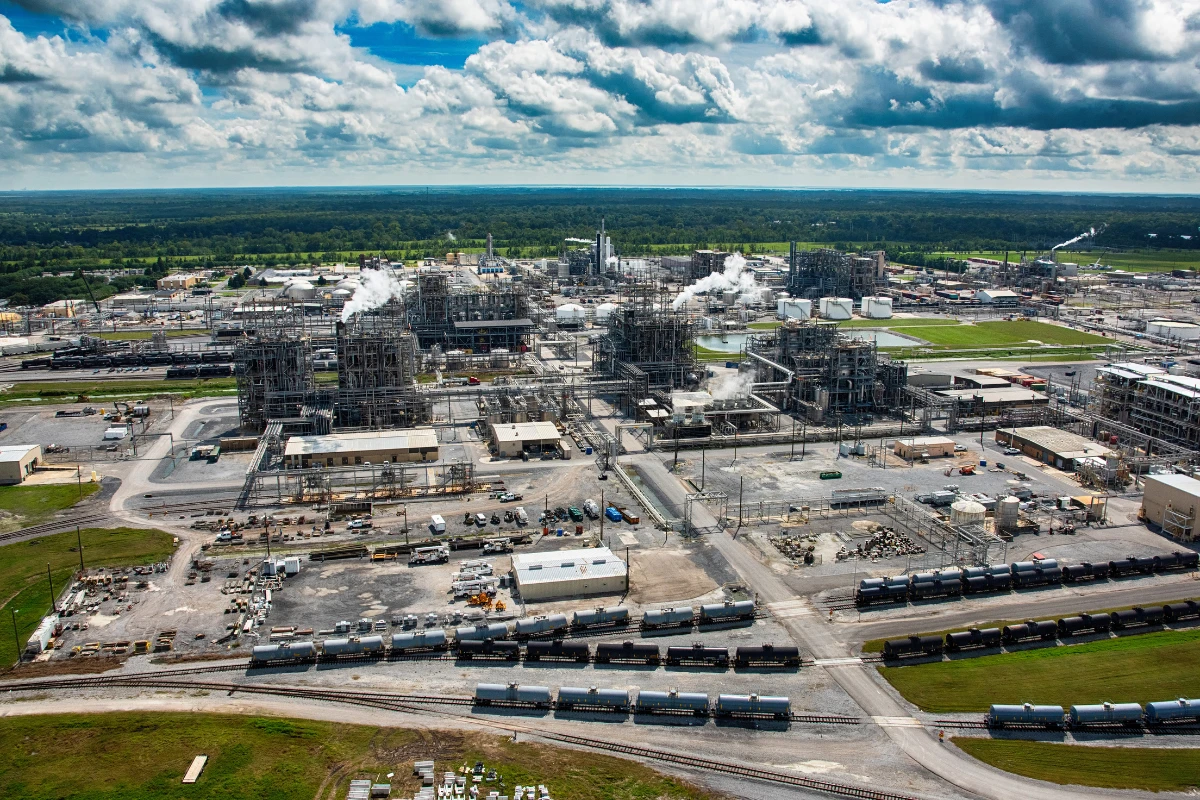
Post-WWII Economic Boom
As the oil and gas industry boomed following WWII, oil refineries and chemical plant workers were heavily exposed to asbestos in Louisiana.

Insulators tore out asbestos insulation on the job, exposing themselves and other workers nearby.
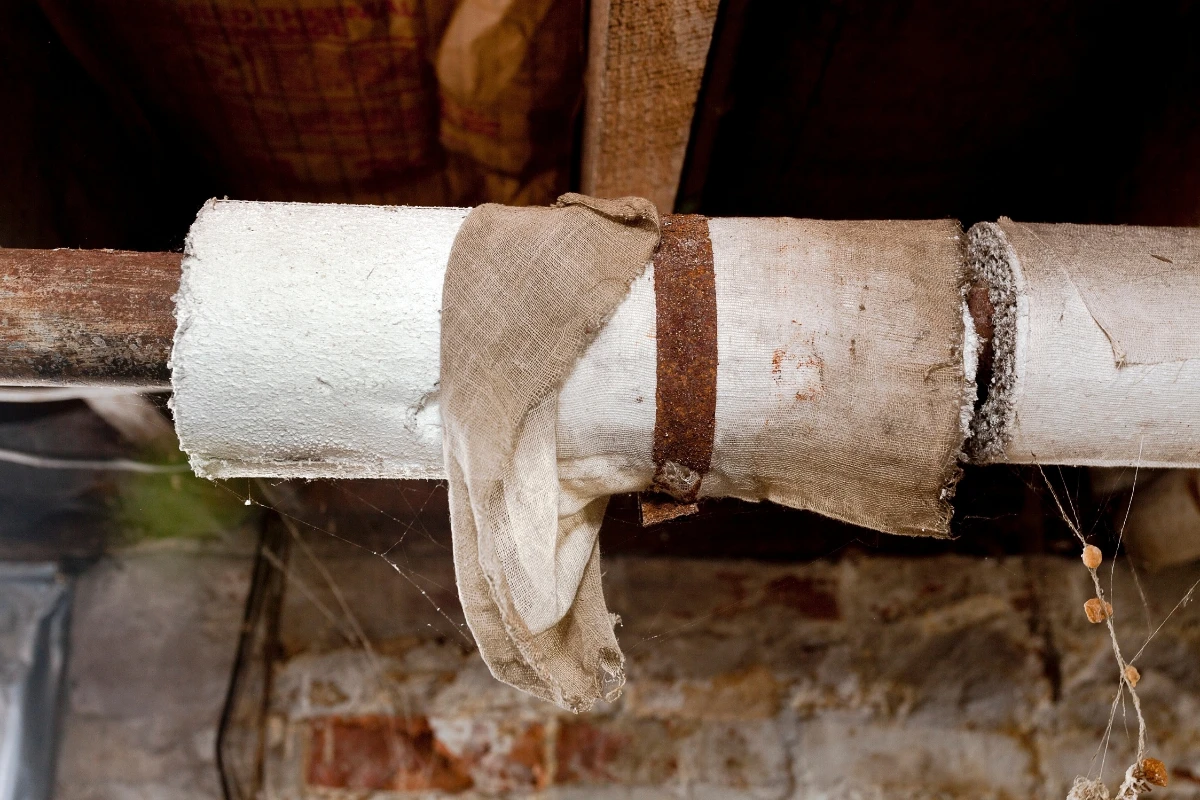

Workers didn’t wear protective masks because they were never told it was dangerous.
1956
Dow Chemical Plant Begins Operation in Plaquemine
The largest petrochemical facility in Louisiana used asbestos extensively.
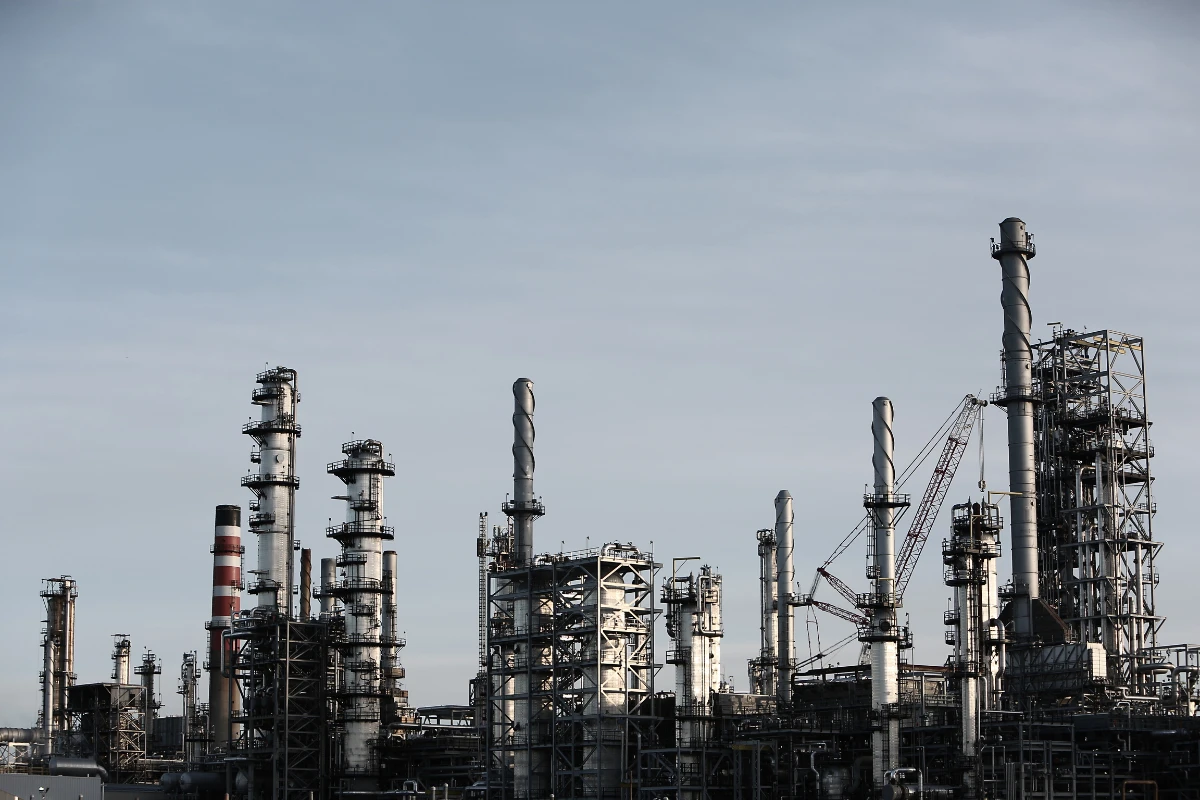

Dow predicted that some of their employees would get cancer from asbestos, but it would be more cost effective to continue using asbestos.
1950s
Shipyard Workers Studied for Asbestos Exposure
Shipyard workers were some of the first studied for asbestos exposure and disease development in the medical & scientific literature dating back to the 1950s.

1950s - 1960s
West Bank Asbestos Exposure
Residents of the West Bank, including the towns of Gretna, Westwego, Harvey, and Marrero, were at risk of exposure to asbestos used in building their driveways and sidewalks.

Manufacturer Johns-Manville sold this asbestos.

The asbestos was so prevalent that white residue would cover cars’ tires as they pulled in and out of driveways.

High winds would blow the asbestos around.
Residents were potentially exposed every time they used a driveway, walked along the sidewalk, or played in the yard.
As a result, many West Bank residents have been sickened with asbestos-related diseases.
1950s - 1960s
Wars and Military Asbestos Use
The U.S. military continued using asbestos heavily during the eras of the Cold, Korean War, and Vietnam War.

Early-1970s
Asbestos Production Peak
By its peak in the early 1970s, asbestos was used in over 6,000 construction and commercial products and applications.

Mid-1970s
Asbestos in Public Buildings
Asbestos-containing materials were used in the construction of public buildings across Louisiana.
- Schools
- Churches
- Hospitals
- Museums
- Libraries
- Airports

1970s
Asbestos Regulations Begin
In the mid-1970s, the government began regulating asbestos to protect workers from asbestos exposure.
The EPA bans use of asbestos in pipe insulation.

Although the government began to acknowledge the health risks of asbestos, public awareness was still in its early stages.
While most chemical companies abandoned asbestos, Dow continued using it. Dow lobbied to oppose the EPA’s proposed ban of asbestos. Dow continued using raw asbestos in U.S. chemical plants.
1986
Asbestos Hazard Emergency Response Act (AHERA)
Schools are required to inspect for asbestos and manage it properly.

1990s-Early 2000s
Legacy Asbestos and Continued Risk
Most asbestos exposure occurred during the repair, renovation, removal, or maintenance of asbestos-containing products that were installed in the mid-20th century.

Trade workers faced ongoing risks of asbestos exposure during roof repairs and plumbing maintenance on older homes and commercial buildings.

Present Day
Asbestos-Related Diseases Impact Workers
Because asbestos-related diseases have long latency periods—from 20 to 60 years—workers exposed decades ago are still developing mesothelioma today.